This guide will walk you through how to CC your cylinder head, explain the importance of accurate measurements, and show you step-by-step how to calculate the compression ratio. By following these instructions and using a Compression Ratio Calculator, you can ensure optimal engine performance, efficiency, and reliability.
What Does “CC’ing a Cylinder Head” Mean?
By knowing the chamber volume, you can calculate compression accurately and make informed decisions about head milling, piston design, or gasket selection.
Why Is CC’ing Important?
- Accurate Compression Ratio
Without knowing the chamber volume, calculating compression is guesswork. Small differences in volume can drastically change the ratio. - Engine Performance
Too much compression can lead to detonation, while too little reduces efficiency and power. Measuring chamber volume helps you stay within safe, effective limits. - Consistency Across Cylinders
Engines rely on balanced performance. CC’ing ensures each cylinder head chamber is equal, minimizing vibration and uneven wear. - Customization for Builds
For performance tuning, cc’ing is essential when selecting pistons, camshafts, or forced induction setups.
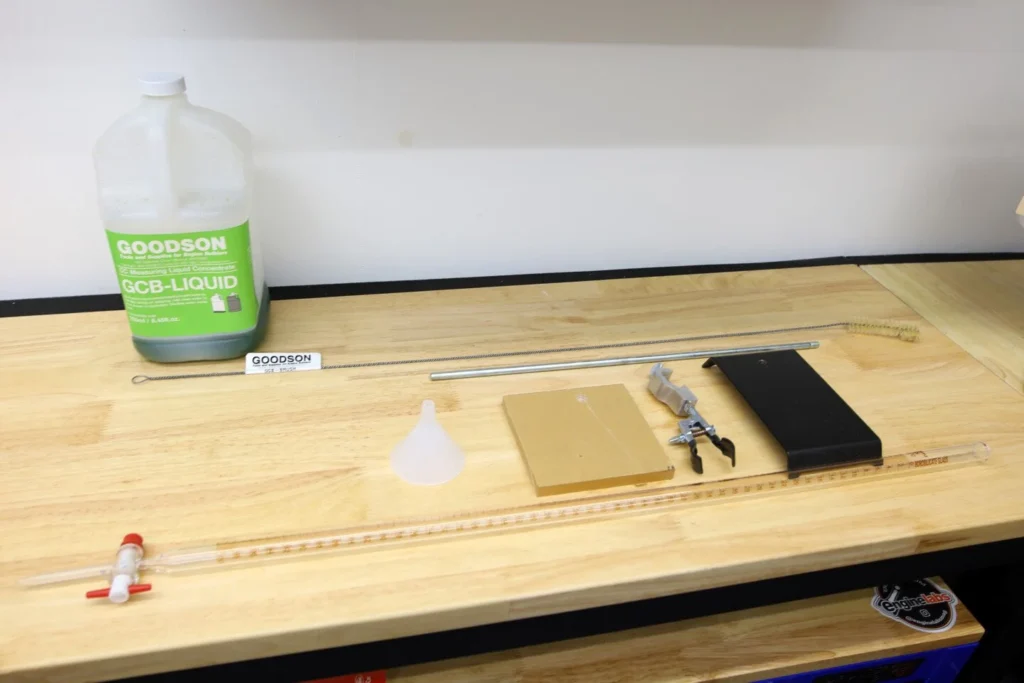
Tools and Materials You Will Need
Before you begin, gather the right tools. CC’ing does not require high-end machines, but it does demand precision and patience.
- Burette or Graduated Cylinder (preferably with 0.1 cc increments)
- Flat Transparent Plate (usually acrylic or plexiglass, with a small fill hole)
- Light Oil, Alcohol, or Dyed Water (fluid for measuring)
- Grease or Petroleum Jelly (to seal surfaces)
- Syringe or Pipette (for transferring fluid)
- Calipers (for verifying dimensions)
- Level Workspace (to ensure accuracy)

Preparing the Cylinder Head
- Clean the Head
Remove carbon deposits, dirt, and oil from the combustion chamber. A clean surface ensures proper sealing. - Install Valves and Spark Plug
CC measurements must reflect the chamber’s true running condition. Ensure valves are seated tightly and spark plugs are in place. - Apply Grease
Lightly coat the valve seats and spark plug threads with grease to prevent leaks during the measurement. - Level the Head
Place the cylinder head on a flat surface so the combustion chamber faces upward. Use a level to ensure accuracy.
Step-by-Step: How to CC a Cylinder Head
Step 1: Position the Plexiglass Plate
Place the transparent plate over the combustion chamber. The plate should cover the chamber completely and be sealed against the head surface with a thin film of grease. Make sure the plate has a small fill hole near the edge.
Step 2: Fill the Burette
Step 3: Remove Air Bubbles
Step 4: Start Filling
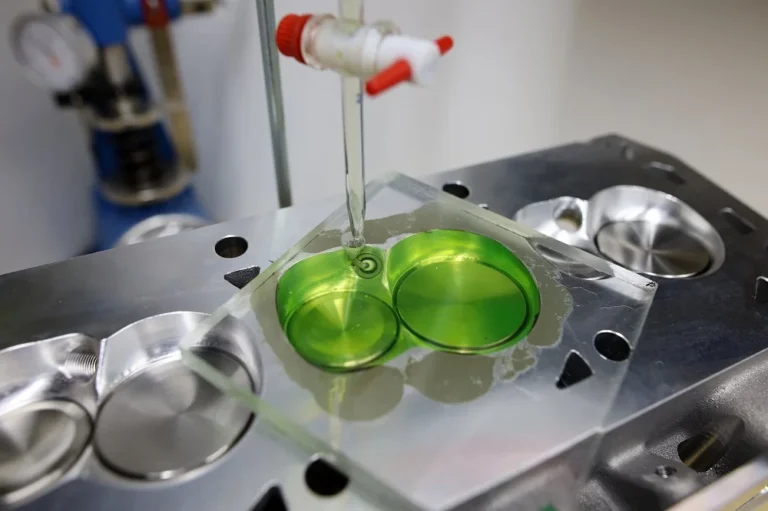
Step 5: Record the Volume
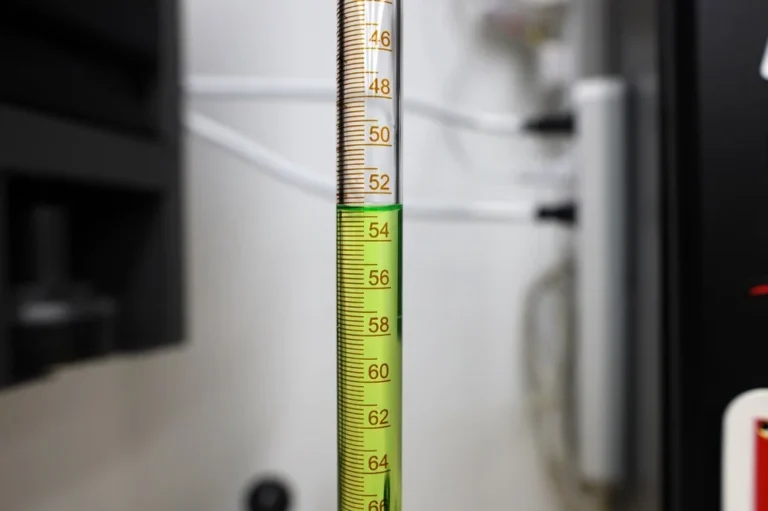

Step 6: Repeat for Accuracy
Calculating Compression Ratio from Chamber Volume
Compression Ratio = (Swept Volume + Clearance Volume) ÷ Clearance Volume
Compression Ratio Calculator
- Swept Volume – The volume displaced by the piston, depending on bore and stroke.
- Cylinder Chamber Volume – The combustion chamber volume measured in cc.
- Piston Dome/Dish Volume – The additional volume from the piston crown shape.
- Gasket Volume – The volume added by the cylinder head gasket.
- Deck Clearance – The volume of the space between the piston at top dead center and the cylinder head.
- Fill in all the required values above.
- Click the Calculate button.
- The calculator will automatically compute and display the Compression Ratio based on your inputs.
Tips for More Accurate CC Measurements
- Use the Same Temperature Liquid: Liquids expand with heat, so keep your measuring fluid at room temperature.
- Work Slowly: Filling too quickly introduces bubbles.
- Record Everything: Keep detailed notes of each chamber measurement for reference.
- Match Chamber Volumes: If chambers differ, you may need to grind or polish to equalize volumes.
- Check Gasket and Piston Shape: Don’t forget these factors, as they also affect compression.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Skipping Valve Installation: Always measure with valves and spark plugs installed, or your readings will be off.
- Not Leveling the Head: An uneven surface causes fluid to pool incorrectly.
- Air Bubbles in the Chamber: Even small bubbles can change the result by several cc.
- Overlooking Chamber Variations: Don’t assume all chambers are identical—measure each one.
When Should You CC Your Cylinder Head?
- Performance Engine Builds
When installing new pistons, camshafts, or boost systems. - Cylinder Head Modifications
After porting, polishing, or milling the head. - Engine Restoration
Ensures you match factory compression ratios. - Custom Gasket or Piston Installation
To verify your final compression ratio matches your intended setup.
Conclusion
Understanding how to cc your cylinder head gives you control over one of the most important aspects of engine building: the compression ratio. While it requires patience and precision, the process is relatively simple with the right tools. By carefully preparing your cylinder head, using accurate measuring techniques, and double-checking results, you can ensure consistent and reliable performance from your engine.
Whether you are a hobbyist builder, a performance enthusiast, or a professional mechanic, learning how to cc a cylinder head is an essential skill. It not only improves your technical knowledge but also ensures that every engine you work on delivers power, reliability, and efficiency.



