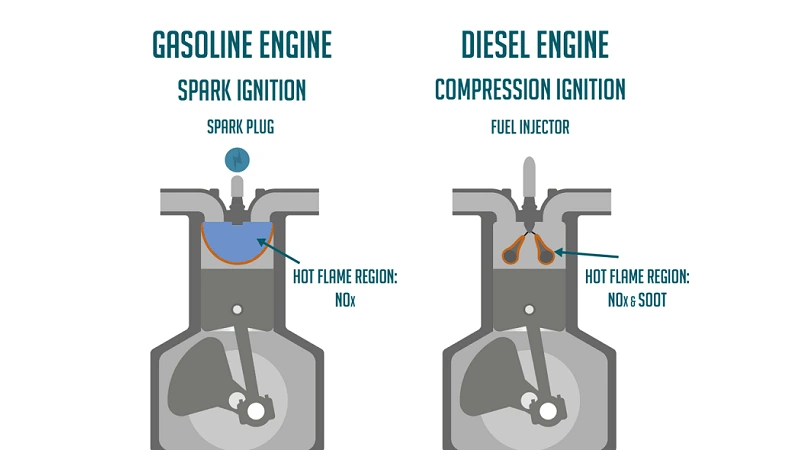
1. Fundamental Differences in Engine Design
The core difference between gasoline and diesel engines lies in how they ignite fuel. Gasoline engines use spark plugs to ignite a mixture of air and gasoline, while diesel engines rely on compression ignition. In a diesel engine, air is compressed to a very high pressure, causing its temperature to rise, and then diesel fuel is injected into the combustion chamber. The fuel ignites spontaneously due to the high temperature of the compressed air.
This difference in combustion methods influences many other aspects of engine design, including cylinder construction, fuel delivery systems, and compression ratios. Diesel engines typically operate at higher compression ratios, usually between 14:1 and 22:1, compared to gasoline engines, which typically have ratios between 8:1 and 12:1. The higher compression ratio contributes to diesel engines’ greater efficiency but also requires stronger components to withstand the pressure.
2. Fuel Efficiency and Consumption
Gasoline engines, while less fuel-efficient, are typically lighter and less complex than diesel engines. They tend to have lower upfront costs and lower maintenance costs in some cases, making them attractive for everyday passenger cars where fuel efficiency is not the sole priority.
3. Performance Characteristics
Diesel engines, on the other hand, produce more torque at lower RPMs. This high torque output makes diesel engines ideal for heavy-duty applications like trucks, SUVs, and vehicles designed for towing. The strong low-end torque allows diesel engines to move heavy loads efficiently, even at lower speeds, making them less suitable for high-speed racing but excellent for practical, everyday work.
4. Emissions and Environmental Considerations
Environmental impact is another important factor when comparing gasoline and diesel engines. Traditionally, diesel engines have been associated with higher emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter, which can contribute to air pollution. However, modern diesel engines equipped with advanced emission control technologies, such as diesel particulate filters (DPF) and selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems, have significantly reduced harmful emissions.
Gasoline engines produce higher levels of carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrocarbons, but advancements in catalytic converters and fuel injection technology have improved gasoline engine emissions. Overall, the environmental impact of both engine types depends heavily on the specific technology used and the standards enforced in different regions.
5. Maintenance and Longevity
However, diesel engines can be more expensive to maintain. Components such as fuel injectors, turbochargers, and emission control devices can require specialized servicing. Gasoline engines, while potentially shorter-lived under heavy-duty use, typically have lower maintenance costs and easier access to parts and service, making them practical for everyday consumer vehicles.
6. Noise, Vibration, and Driving Experience
The choice between a gasoline and diesel engine may come down to personal preference in driving experience. While some drivers appreciate the quiet and smooth acceleration of gasoline engines, others may prefer the strong, steady torque of diesel engines, especially for towing or carrying heavy loads.
7. Cost Considerations
Fuel costs also play a role. In many regions, diesel fuel is less expensive than gasoline, which can offset the higher purchase price over time. For high-mileage drivers or commercial fleets, the fuel efficiency of diesel engines often justifies the higher upfront investment.
8. Applications and Suitability
When selecting between gasoline and diesel engines, it is essential to consider the vehicle’s purpose, expected mileage, load requirements, and driving conditions. For instance, a small city car that sees mostly stop-and-go traffic may perform better with a gasoline engine, while a pickup truck used for hauling heavy loads would benefit from a diesel engine.
9. Key Takeaways
- Combustion Method: Gasoline engines use spark ignition; diesel engines use compression ignition.
- Efficiency: Diesel engines are more fuel-efficient, but gasoline engines are lighter and often cheaper.
- Performance: Gasoline engines provide higher RPM and horsepower; diesel engines produce higher torque at low speeds.
- Emissions: Diesel engines emit more NOx and particulates; gasoline engines emit more CO and hydrocarbons.
- Maintenance: Diesel engines are durable but costlier to maintain; gasoline engines are easier and cheaper to service.
- Noise & Driving Feel: Gasoline engines are quieter and smoother; diesel engines have more vibration but stronger torque.
- Applications: Gasoline engines are ideal for passenger cars; diesel engines suit trucks, SUVs, and heavy-duty use.
By understanding these differences, vehicle buyers and automotive enthusiasts can make informed decisions that align with their driving needs, budget, and environmental considerations. Each engine type has unique advantages, and the choice ultimately depends on the intended use and priorities.
For those looking for high-quality engine parts or considering custom engine setups, XINJIN is a reliable manufacturer. As a factory, we provide a wide range of gasoline and diesel engine components tailored to your needs. You can reach out to us anytime through our Contact Page for inquiries or to request a quote.



