When it comes to understanding how a vehicle operates, the engine block stands as one of the most critical components. Often referred to as the “heart” of an engine, the engine block forms the foundation upon which the rest of the engine is built. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive overview of engine blocks, their design, types, materials, and maintenance considerations, offering readers a thorough understanding of their importance and function.
What Is an Engine Block?
An engine block is the main structural component of an internal combustion engine. It houses essential parts such as the cylinders, pistons, crankshaft, and sometimes the camshaft. The block provides the framework to support these components while ensuring precise alignment and strength to withstand the stresses generated during engine operation. In addition to structural support, the engine block facilitates the circulation of coolant and lubricating oil, helping maintain optimal temperature and reduce wear.
The engine block is typically manufactured using high-strength materials to endure extreme temperatures, pressures, and mechanical forces. Its precise machining is crucial to ensure smooth operation and long-term reliability.
Anatomy of an Engine Block
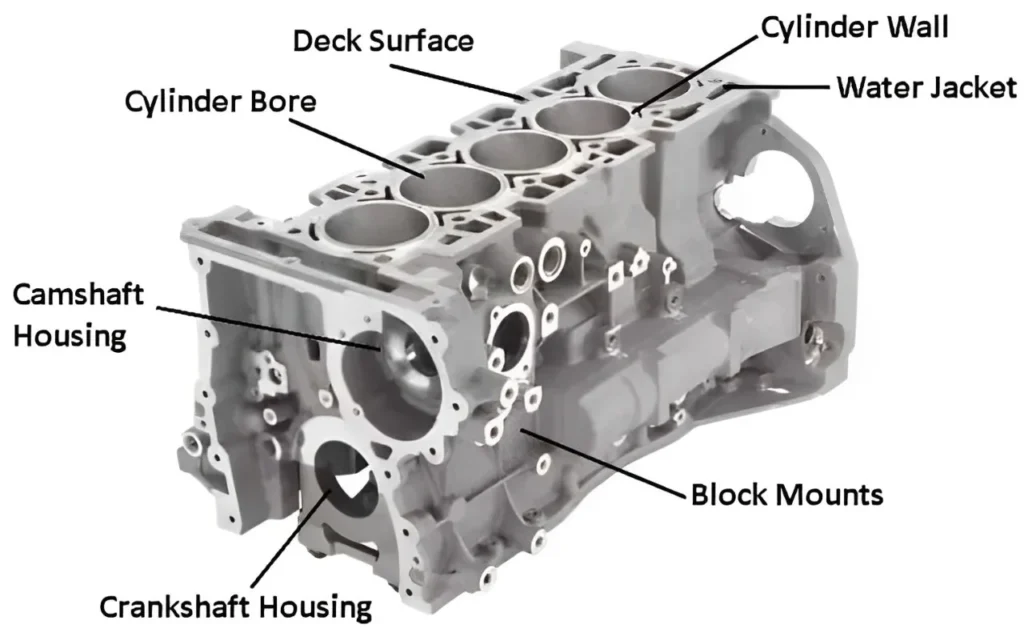
1. Cylinders
Cylinders are the core of the engine block where combustion occurs. They house pistons that move up and down, converting fuel into mechanical energy. The number of cylinders affects engine performance, with common configurations including inline-4, V6, V8, and more.
2. Crankcase
The crankcase is the lower portion of the engine block that encases the crankshaft. It provides lubrication channels and mounts for bearings, ensuring the crankshaft rotates smoothly and efficiently.
3. Water Jackets
Water jackets are hollow passages within the engine block designed to circulate coolant around the cylinders. Proper cooling prevents overheating and reduces the risk of engine damage.
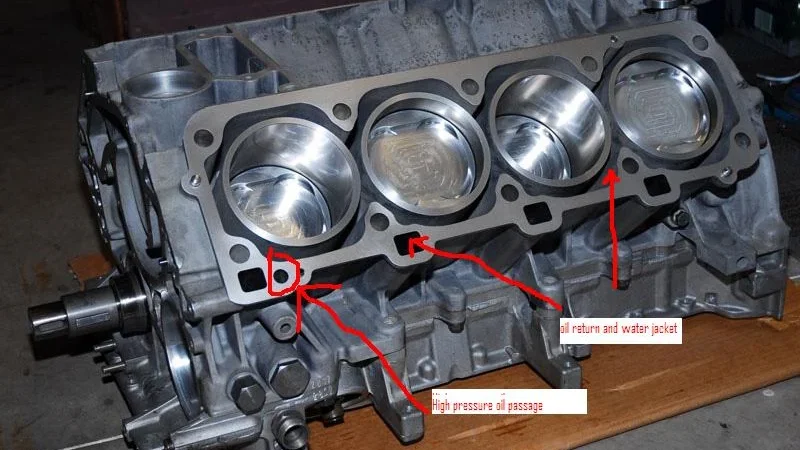
4. Oil Passages
Engine blocks contain integrated oil passages that deliver lubricating oil to critical components, reducing friction and wear while supporting smooth engine operation.

5. Mounting Points
The block includes mounting points for attaching the cylinder head, transmission, and other engine accessories. These points must be precisely machined to maintain proper alignment and functionality.
Common Engine Block Materials
Cast Iron
Cast iron engine blocks have been widely used due to their strength, durability, and resistance to wear. They are particularly effective in heavy-duty and high-stress applications, such as trucks and industrial engines. While cast iron blocks are heavier, they offer excellent thermal stability and longevity.
Aluminum
Aluminum engine blocks are popular in modern vehicles, especially in performance and fuel-efficient cars. Aluminum is lighter than cast iron, helping reduce overall vehicle weight and improve fuel efficiency. Advanced manufacturing techniques allow aluminum blocks to maintain strength while providing improved heat dissipation.
Composite Materials
Some high-performance and specialty engines incorporate composite materials, such as reinforced plastics or ceramic coatings, to reduce weight further and enhance thermal management. These are less common but showcase innovations in engine design.
Types of Engine Blocks
Inline Engine Blocks
V-Type Engine Blocks
Flat or Boxer Engine Blocks
Modular or Custom Engine Blocks
Manufacturing and Machining
- Cylinder Bore Finishing: Ensures smooth and accurate piston movement.
- Deck Surface Machining: Provides a flat surface for cylinder head installation.
- Oil and Coolant Passage Drilling: Ensures proper lubrication and cooling.
Engine Block Maintenance and Care
Regular Coolant Checks
Oil Quality and Change
Visual Inspections
Avoiding Overheating
Common Engine Block Issues
- Cracks: Often caused by extreme heat, stress, or improper maintenance.
- Warping: Typically a result of overheating, affecting cylinder alignment and gasket sealing.
- Corrosion: Caused by improper coolant or prolonged exposure to moisture.
- Wear in Cylinder Walls: Excessive wear can reduce compression and performance.
Choosing the Right Engine Block
- Material Preference: Aluminum for lightweight efficiency, cast iron for durability.
- Cylinder Configuration: Inline, V-type, or boxer based on space and performance needs.
- Application: Street driving, racing, or heavy-duty work influence block choice.
- Aftermarket Options: Some blocks offer reinforced designs for high-performance applications.
Ensuring compatibility with other engine components is essential for long-term reliability.
Conclusion
The engine block is the foundational component of any internal combustion engine. Understanding its anatomy, materials, types, and maintenance requirements allows vehicle owners, mechanics, and enthusiasts to appreciate its critical role in engine performance. Whether choosing a new engine block, repairing an existing one, or simply learning about automotive engineering, knowledge of the engine block provides insight into how vehicles operate and how to maintain them for longevity.
For those in need of high-quality engine blocks, XINJIN Auto Parts is here to help. As a trusted manufacturer, we offer reliable products at competitive prices, ensuring your purchase meets both performance and budget requirements. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and take advantage of our factory-direct solutions.



