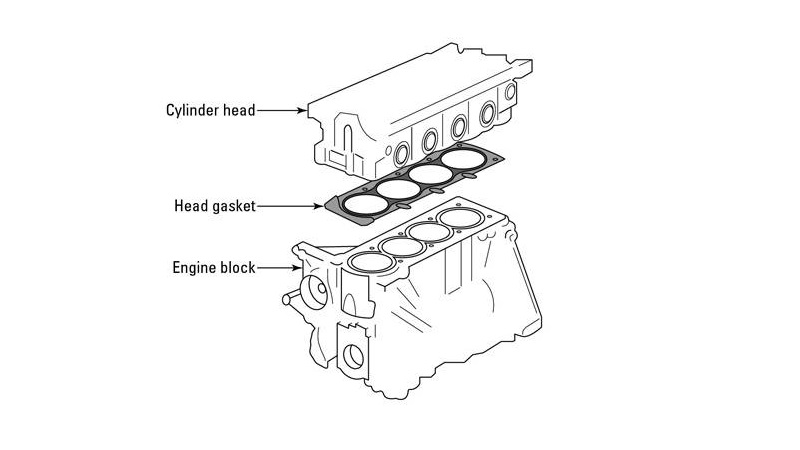
What Is a Block Cylinder Head?
- The engine block serves as the foundation of the engine. It houses the cylinders, pistons, crankshaft, and connecting rods.
- The cylinder head, on the other hand, sits atop the engine block, sealing the combustion chambers and accommodating components such as valves, spark plugs, and fuel injectors.
Structural Composition of the Block Cylinder Head
- Cast Iron: Known for strength and durability, often used in heavy-duty engines.
- Aluminum Alloy: Lighter and provides better heat dissipation, commonly used in modern vehicles.
- Cylinders are precisely machined to fit the pistons.
- Coolant passages circulate fluid to maintain optimal temperature.
- Oil channels deliver lubrication to reduce friction.
- The intake and exhaust valves control airflow.
- Spark plugs or injectors (depending on fuel type) initiate combustion.
- Camshafts (in overhead cam designs) regulate valve timing.
The seamless interaction between these components ensures smooth combustion, minimal energy loss, and consistent power delivery.
How the Block Cylinder Head Works
- Compression and Combustion: The cylinder head seals the combustion chamber, enabling the compression of the air-fuel mixture. When ignition occurs, the resulting explosion pushes the piston downward to produce power.
- Heat Management: Both the engine block and cylinder head have coolant channels to prevent overheating. Proper heat dissipation is vital for maintaining efficiency and preventing warping or cracking.
- Lubrication: Oil circulates through the engine block and cylinder head, reducing wear between moving parts like the crankshaft, camshaft, and valves.
- Gas Exchange: The intake valves draw in the air-fuel mixture, while exhaust valves release burned gases. This synchronized exchange is controlled by camshafts and timing belts or chains.
Without precise cooperation between the engine block and cylinder head, the engine cannot function properly.
Common Problems with Block Cylinder Heads
(1) Cylinder Head Gasket Failure
(2) Cracked Cylinder Head
(3) Warped Engine Block
(4) Valve and Camshaft Wear
(5) Corrosion and Deposits
How to Identify Symptoms of Block Cylinder Head Damage
- White or blue smoke from exhaust
- Coolant loss without visible leakage
- Engine misfires or rough idling
- Oil contamination (milky oil texture)
- Overheating during normal operation
- Unusual knocking or tapping noises
If any of these symptoms appear, it’s crucial to perform a cylinder head inspection or engine compression test to confirm the source of the problem.
Maintenance Tips to Extend Engine Life
- Use high-quality coolant and oil: Poor fluids accelerate wear and corrosion.
- Maintain proper torque on head bolts: Improper tightening can lead to gasket failure.
- Flush cooling systems regularly: Prevents scale and deposit buildup.
- Monitor temperature gauges: Early detection of overheating saves the engine block from damage.
- Replace head gasket when needed: Do not ignore minor leaks or overheating signs.
Consistent care reduces the chance of expensive engine block repair or full rebuilds.
Professional Repair vs. Replacement
- Repair: Suitable for minor cracks, gasket leaks, or worn valve seats. Techniques include resurfacing, welding, and pressure testing.
- Replacement: Recommended for severe cracking, extensive warping, or structural failure. A remanufactured cylinder head or engine block assembly offers reliability similar to new components.
A professional mechanic can perform pressure testing and precision measurements to determine whether a rebuild or replacement is the better solution.
Why Quality Matters in Block Cylinder Head Manufacturing
The quality of the engine block and cylinder head directly influences performance, efficiency, and longevity. High-quality casting, precise machining, and thorough inspection ensure proper alignment and sealing between both components.
Manufacturers that specialize in precision machining and quality control often produce cylinder heads that outperform cheaper alternatives in durability and reliability. For B2B buyers or automotive rebuilders, investing in certified engine block cylinder head assemblies ensures consistent engine performance and customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
The block cylinder head represents the foundation of every internal combustion engine. Its structure, from the precision of the cylinder bores to the sealing of the head gasket, determines how efficiently the engine performs.
By understanding its composition, recognizing common problems early, and following proper maintenance practices, you can significantly extend the lifespan of your engine and prevent major failures. Whether for repair, replacement, or performance optimization, paying attention to the engine block cylinder head is key to achieving long-term reliability and efficiency.



