Piston rings may seem like small, inconspicuous parts, but they are the unsung heroes of your car’s engine. They perform a vital function that ensures your engine’s efficiency, power, and longevity. In this video, we’re going to learn how piston rings work and how they contribute to the overall performance of your vehicle.

What Are Piston Rings?
A piston ring is a metallic split ring that is attached to the outer diameter of a piston in an internal combustion engine. They are typically positioned in grooves or slots on the piston itself. These rings serve as a sealing mechanism between the piston and the inner walls of the engine’s cylinder.
Piston rings ensure that the combustion chamber, where fuel and air ignite to produce power, remains sealed during the engine’s operation. This seal prevents any gas from escaping or oil from entering where it shouldn’t be. This sealing action is essential for engine efficiency and performance.
The main functions of piston rings in engines is that it seals the combustion chamber so that there is minimal loss of gases to the crankcase. Improves heat transfer from the piston to the cylinder wall. It maintains proper quantity of the oil between the piston and the cylinder wall.
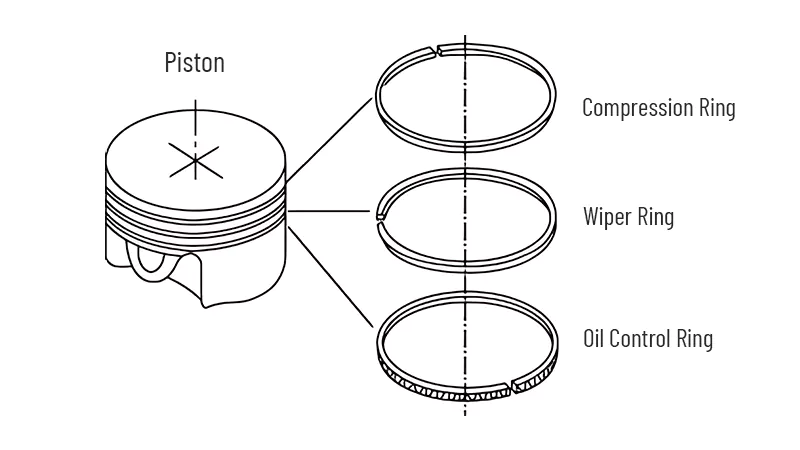
Types of Piston Rings
Regulates engine oil consumption by scraping oil from the cylinder walls back to the sump. Automotive piston engines typically have three rings per cylinder. The top ring known as a compression ring.
The middle ring is a second compression ring that is also known as wiper ring. And the bottom ring is known as the oil control ring. Compression rings are located near the top of the piston, usually in the first ring groove.
Compression Rings
Their primary function is to create an airtight seal between the piston and the cylinder wall during the compression stroke of the engine. During the compression stroke, these rings prevent the high pressure air fuel mixture from escaping past the piston and into the crankcase. This seal is essential for maintaining compression, which is crucial for engine power and efficiency.
Wiper Ring
The wiper ring, also called a napier ring or backup compression ring, is installed below the compression ring. To understand its functions, we first need to understand the functions of oil control ring. Oil control rings regulate the distribution of lubricating oil along the cylinder wall and preventing excess oil from entering the combustion chamber, which could lead to increased oil consumption, incomplete combustion, and increased emissions.
The main function of a wiper ring is to clean the liner surface off the excess oil and to act as support backup ring on stopping any gas leakage further down, which escaped the top compression ring. Most of the wiper rings have a taper angle face, which is positioned toward the bottom to provide a wiping action as the piston moves toward the crankshaft.
Oil Control Rings
Oil control rings often consist of multiple components, including a thin expander and scrapers. The expander helps maintain tension, while the scraper and wiper components control oil and ensure proper lubrication. These rings are also used to spread the oil evenly around the circumference of the liner.
The oil is splashed onto the cylinder walls. These rings are also called scraper rings as they scrap the oil off the cylinder walls and send back to the crankcase. In the oil ring, holes or slots are cut into the radial center of the ring which allows the excess oil to flow back to the reservoir.
Oil rings can be one piece or two pieces. To increase the contact pressure between the ring and the liner surface, the rings can have chamfered edges on either the outer sides of the lands or facing the combustion chamber to reduce the oil consumption through improved oil scraping from the bore. Two-piece oil control rings consist of a cast iron or profiled steel ring and a coil spring, which is made from heat-resistant spring steel to act around the whole ring circumference for maintaining the pressure and contact.
Materials Used in Piston Rings
One of the most prominent materials used in making piston rings is cast iron. This is because it contains graphite in the lamellar form, which itself acts as a lubricant, assisting the sliding motion between the rings and the liner.
Alloys and coatings are done on the piston rings and it will vary as per the type of the ring, as the functionality of these rings are different from each other. The most common form of alloying cast iron is chromium, molybdenum, vanadium, titanium, nickel, and copper. The piston ring material is kept harder than the cylinder liner to provide maximum life.
Why Piston Rings Fail?
Why piston rings fail? The combustion chamber exerts tremendous pressure on the piston rings. If the combustion pressure of the gas produced inside the chamber is higher than the usual, it may affect the ring performance. This can be due to detonation and pinging of the fuel from the leaky injector or when the fuel is mixed with dirty air.
Contaminated fuel oil or wrong grade of cylinder oil will also affect the performance of the ring. As the ring starts wearing down, their ability to seal the combustion gases will become apparent. Bad fuel or cylinder oil quality, bad combustion process, wrong fuel timing, worn liner, etc., are the normal cause of piston rings worn out.
Blow-by
The most common indication of a worn ring is gas passing into the crankcase or under piston area known as blow-by. Sticky ring due to carbon or sludge deposit and breaking or crack on the ring can result due to wear down. Blow-by is the escape of combustion gases from the engine’s combustion chamber past the piston rings and into the crankcase.
It occurs due to imperfect sealing between the piston rings and cylinder walls, leading to decreased engine efficiency, increased oil consumption, and higher emissions. Excessive blow-by indicates engine wear and may require repairs. Blow-by can have several consequences like reduced engine efficiency and increased oil contamination.
Blow-by can lead to higher emissions of pollutants since unburned fuel and combustion by-products are not properly contained within the combustion chamber. Similar to all the other machinery parts, the piston ring will also have a set time period of overhaul and replacement. The life of a piston ring entirely depends on the piston ring type, the size of the engine it is fitted on, and the operational condition of the ring and the liner.
Lifespan of Piston Rings
In a well-maintained passenger car, driven under normal conditions, piston rings can generally last between 75,000 to 100,000 miles or more before significant wear occurs. However, it’s important to note that this is a general estimate, and actual ring life can vary. Some engines might see rings lasting well beyond 100,000 miles with proper care, while others might experience wear earlier, especially if subjected to harsh operating conditions or inadequate maintenance.
Conclusion
Although piston rings are small components inside an engine, they play a critical role. The three piston rings—the compression ring, wiper ring, and oil control ring—work together to ensure the engine remains sealed under high pressure and temperature, minimizes oil consumption, and maintains proper lubrication and heat transfer. Their condition directly affects engine power, fuel efficiency, and durability.
At XINJIN, we specialize in engine assemblies, cylinder heads, and engine blocks. We uphold high manufacturing standards and strict quality control to provide our clients with dependable core engine components. Whether you need bulk supply or customized solutions, we can offer products tailored to your requirements. If you are looking for a trusted partner for engines and critical engine parts, contact us today.



