When exploring vehicle specifications or discussing engine performance, the term “cylinder” frequently arises. It’s a fundamental component of any internal combustion engine, yet it’s often misunderstood by non-specialists. Whether you’re choosing between a 4-cylinder or a 6-cylinder vehicle, understanding how cylinders work and what they mean for performance, efficiency, and reliability is essential.
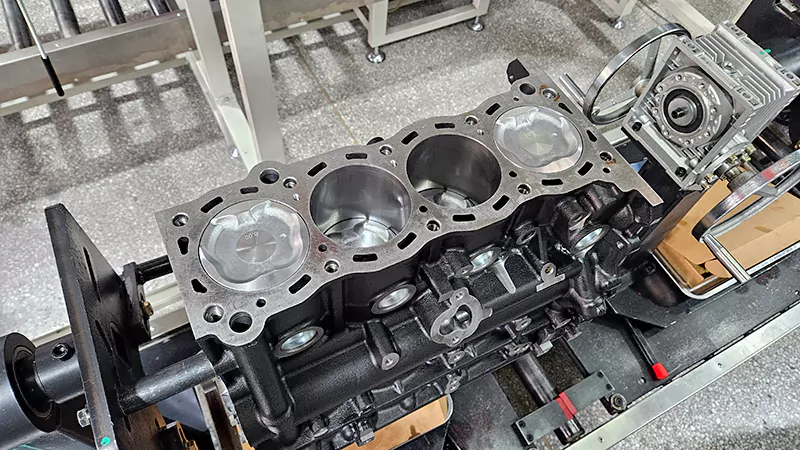
What Is an Engine Cylinder?
An engine cylinder is a central part of an internal combustion engine. It’s a cylindrical chamber where fuel combustion occurs to produce mechanical energy.
Each cylinder contains a piston that moves in a precise up-and-down motion. Here’s a breakdown of the combustion cycle that powers your vehicle:
- Intake Stroke – The piston moves downward, drawing in an air-fuel mixture.
- Compression Stroke – The piston moves upward, compressing the mixture.
- Power Stroke – A spark plug ignites the compressed mixture, causing an explosion that forces the piston downward.
- Exhaust Stroke – The piston moves up again, expelling exhaust gases from the combustion chamber.
This four-stroke cycle happens rapidly and continuously in each cylinder, generating the rotational force that turns the crankshaft and powers the vehicle.
4-Cylinder vs 6-Cylinder Engines
Power Output and Performance
The number of cylinders determines how many combustion events occur per revolution of the crankshaft, directly affecting engine power. A 6-cylinder engine, with two additional combustion chambers compared to a 4-cylinder, produces more torque and horsepower, especially beneficial for:
- Towing
- Performance driving
- Larger vehicles (SUVs, trucks, full-size sedans)
However, modern 4-cylinder engines—especially those with turbocharging or direct injection—can deliver impressive power while maintaining a compact size and lower weight.
Fuel Efficiency
In general:
- 4-cylinder engines are more fuel-efficient due to lower internal friction, reduced weight, and lower displacement.
- 6-cylinder engines consume more fuel, but advancements such as cylinder deactivation and variable valve timing have narrowed the gap.
For example, a current-generation turbocharged 4-cylinder engine may offer better fuel economy and similar output compared to a naturally aspirated 6-cylinder from a decade ago.
Reliability and Maintenance
Reliability is often a concern in the 4-cylinder vs 6-cylinder debate. Here’s how they compare:
4-Cylinder Engines
- Fewer moving parts
- Lower long-term maintenance costs
- Often easier and cheaper to repair
6-Cylinder Engines
- Can be more durable under heavy loads and high performance demands
- More components may increase repair complexity and cost
That said, engineering quality and regular maintenance have a greater impact on reliability than cylinder count alone.
Configuration Matters Inline vs V-Type
Engine cylinders can be arranged in different ways:
- Inline (I4, I6): Cylinders are arranged in a straight line. Common in smaller engines due to simplicity and compactness.
- V-Configuration (V6, V8): Cylinders are split into two angled banks forming a “V” shape. This configuration allows for more cylinders in a shorter space and smoother operation.
- Flat (Boxer): Cylinders lie flat and oppose each other. Known for a low center of gravity and used in brands like Subaru and Porsche.
Which Engine Should You Choose?
Consider a 4-Cylinder Engine if you:
- Prioritize fuel economy and lower emissions
- Drive mostly in cities or at moderate speeds
- Prefer a lighter, more affordable vehicle
Consider a 6-Cylinder Engine if you:
- Need more power for towing, acceleration, or off-road
- Drive longer distances or on highways
- Own a larger vehicle or frequently carry passengers/cargo
Conclusion
Engine cylinders remain a core aspect of vehicle performance, but modern automotive engineering has transformed the way we evaluate them. Cylinder count is no longer the sole indicator of power or efficiency.
Understanding how cylinders function—and how engine layout, technology, and use case intersect—will help you make informed decisions whether you’re purchasing a car, building one, or simply trying to understand what makes your vehicle tick.
Looking for a trusted supplier of engine assemblies, cylinder heads, or blocks?
We are a B2B manufacturer specializing in high-quality engine components for global clients. Contact us for details.



